Founder Mutations
is the genetic legacy of a founder of a population, which is passed on through
inheritance. People who have founder mutations have damaged DNA embedded in a
larger stretch of DNA that is identical to that of the founders. This region of
shared DNA is called a haplotype. If you share a haplotype with someone then
that means that you guys share a common ancestor and are related. One can
determine the age of a founding mutation by the length of the haplotype because
over time the haplotype becomes shorter. The haplotype in the founder is an
entire chromosome that contains the mutation. The hot spot is different because
it is a DNA base pair that is prone to mutation. People who have hot spots are
not related, so the rest of their DNA varies, unlike in people who have the
founder mutation that do share some DNA.
The reason people
have genetic mutations is because the mutations gives people an advantage in
warding off diseases. If you have the dominant trait of a mutation you could
have an unwanted disease, but if you have the recessive trait, that will help
you. People who carry a single copy of the sickle cell disease are much less
likely to contract malaria. Individuals with two copies of the mutation die off
soon, but people with one copy live longer because their copy helps them fight
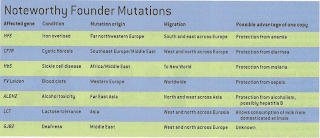
off diseases. This is called balancing selection. This chart will give more
examples of how mutations can help:
The
ability of identifying founder mutations helps doctors identify certain
patients to be tested for diseases. Also, geneticists can use the haplotype to
trace back the origins of populations and their migration tracks. They can look
back at a certain time and region to help find the connections between all
humans.

No comments:
Post a Comment